There are many ways to build a software product, and there’s no one-size-fits-all solution.
This guide is here to help you decide how to choose a tech stack by highlighting the essential factors to consider when selecting the technology stack for a web or mobile development project. We will cover:
- The key components of a tech stack
- A step-by-step process for selecting a tech stack tailored to your project’s specific requirements
- Analysis of tech stack choices made by well-known companies.
At Syndicode, we approach tech stack selection with great care, and our clients reap the benefits. MedYouCate, SwiftComply, and Instalinks are just some of the projects that have benefited from our tech stack consulting and subsequent development services.
What is a tech stack?
A tech stack, short for “technology stack,” combines software tools and technologies used to build and run software applications. It comprises programming languages, frameworks, libraries, databases, and other software tools and technologies stacked together for use by development teams.
For example, a common web development tech stack may include components like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for the front end, a backend framework like Ruby on Rails, Django for Python, or Express.js for Node.js, and a database system like MySQL or PostgreSQL.
Different software types, such as web applications, mobile apps, or desktop software, require different tech stacks to meet their unique needs. Therefore, how you choose a technology stack should be based on the project’s specific requirements and goals.
Factors to consider when choosing a tech stack
Deciding how to choose a tech stack is a crucial step for any software project. Your decision should be based on a thorough assessment of your project’s needs, your team’s skills, and the current market conditions.
Project requirements
The specific functionality and features your project requires will often dictate the choice of technology. For example, if the project involves building a real-time chat application, you’ll need technologies like WebSockets to make it work effectively.
Moreover, some programming languages and frameworks are better suited for handling performance and scalability demands. Thus, microservices architecture, containerization (such as Docker), and cloud services can efficiently handle high workloads and scale horizontally.
On the other hand, if your project is small, simple, and unlikely to undergo frequent changes, monolithic architecture and a simple language like PHP can be a cost-effective option for both development and maintenance.
Team expertise
It’s generally a good idea to make the most of your software development team’s existing knowledge and skills. When developers work with technologies they are already familiar with, it results in higher productivity, efficient coding, and better decision-making.
However, sometimes projects require new technologies or frameworks due to specific needs or industry trends. In such cases, consider engaging external specialists to work alongside your core team.
This way, you will allow your team members to learn and gain expertise in the new tech stack. The key here is to ensure that the new technology aligns well with what your team is already comfortable with. This approach minimizes the learning curve and keeps your team motivated.
Alternatively, you can outsource your entire project to a reputable software development partner that specializes in creating applications similar to yours.
Read also: What are software development outsourcing and outstaffing?
Market trends
Staying ahead of the curve by embracing a trending technology can give your project a competitive edge. This can translate into innovative features, an enhanced user experience, or improved security.
Moreover, when you opt for a web development tech stack in high demand, you increase your chances of finding skilled developers who are well-versed in that particular stack. Conversely, selecting an outdated or niche technology may pose challenges in recruiting and retaining talent.
Additionally, market trends impact the availability of third-party integrations and libraries. Choosing a popular tech stack often means you’ll have access to a wider range of tools and services that can streamline the development process.
Is tech stack really that important?
Oh, yes. The choice of a tech stack can significantly impact your business success, and our specialists ensure your project receives everything it needs. Discover how our clients have benefited from our advice and expertise.
See projectsHow to choose a tech stack?
Selecting the relevant web development stack is a critical decision that can significantly impact your project’s success, development efficiency, costs, security, and long-term sustainability. To make an informed and practical choice, follow these steps:
Step 1. Assess your current technology
Chances are, your business already has some IT infrastructure in place unless you’re just starting out. It’s a good idea to take a closer look at the tech tools you’re using and how a new software project fits into the picture.
To do this, gather your development team and list the technologies and components you currently have.
The next move is to evaluate your tech stack by answering these questions:
- Do all components of your tech stack integrate well with each other?
- Does your current tech stack help you achieve organizational goals?
- Does it streamline workflows for greater efficiency?
- Does your current software provide a positive user experience?
It’s a smart decision to get an external IT consultant to provide a fresh perspective on how you can enhance your tech setup with minimal effort.
Once you’ve identified the strengths and weaknesses of your current tech tools and have a plan for improvement or switching to a new tech setup, you’re ready to move forward.
Step 2. Assess the skills at hand
First, take a look at the skills within your current team. What frameworks and programming languages are they good at? It’s usually wise to let your development specialist decide how to choose the tech stack. Working with familiar technologies gives you better control over the development process.
If you decide to outsource the development work, we recommend choosing a development partner based on your comfort level in working with them and leaving the question of how to select a technology stack up to them.
Here’s a list of key factors to consider when selecting a software development company:
- Experience in creating and maintaining solutions similar to your project. Check their portfolio, website, and social media profiles for any evidence of their credibility.
- Client satisfaction. Read testimonials from former and current clients on reliable platforms like Clutch. Analyze what clients highlight as the company’s strengths in the testimonials, and note any concerning feedback or aspects that weren’t mentioned.
- Communication. Contact the potential partner and schedule a meeting or call. Ask about their delivery model, team expertise, technologies they use, pricing, and any other questions you may have following your research. See whether their work approach aligns with your needs and whether you feel comfortable understanding the information they provide.
- After-launch support. Ensure that they can offer ongoing maintenance services once your product goes live. If your project is expected to evolve over time, ask if the development partner can scale the development team to accommodate the growing needs.
- Security. Ask how they will protect your data, including information about your business and project. Data security is typically ensured by signing a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA). Development security practices, in turn, should include data encryption techniques and protocols, quality assurance, and regular software updates. In addition, discuss secure methods for exchanging information, whether through email, messenger applications, or other means.
Read also: Why is quality assurance important?
Step 3. Look at your project requirements
Review the unique needs of your project and assess how they align with the vendor’s skills and the considered tech stack. If your current technology setup doesn’t fully meet the project’s requirements, you may consider expanding it with new components, libraries, or modules.
Additionally, you might discover other technologies, frameworks, or libraries that work well with your current tech setup and can help address gaps.
Alternatively, you can decide to migrate to a new tech stack.
When evaluating project requirements, consider the following:
- Compatibility of the tech stack’s capabilities with your project’s needs;
- Scalability. Can the stack handle the expected growth in users and data without major rearchitecting?
- Performance. Is the stack capable of delivering the required performance, response times, and throughput for your application?
- Security. Does the stack have the necessary security features and mechanisms to protect against common threats and vulnerabilities?
- Cost. Consider the licensing, hosting, and maintenance costs associated with the tech stack. Ensure it fits your budget.
- Development speed. Will the stack enable efficient and rapid development, or is there a risk of running into unnecessary complexity and delays?
- Community and support. Evaluate the stack’s community support and available resources (documentation, forums, etc.) for problem-solving and troubleshooting.
Step 4. Evaluate the popularity of the tech stack
The more widely used a tech stack is, the easier it is to find developers. Here’s the catch, though: some tech stacks have only gained popularity in recent years, which means that most developers working with them are relatively new to the field.
This isn’t necessarily a drawback, as not all projects require the expertise of a senior developer. In addition, junior developers usually charge less for their services. But you must be absolutely certain that your project is simple enough for a junior team to handle.
Otherwise, you risk missing deadlines and implementing unconventional solutions for something that could be done simply.
Here’s how to assess the popularity of a tech stack:
- Explore online surveys and reports published by tech organizations, companies, and developer communities that highlight popular languages, frameworks, and libraries. Examples include the Stack Overflow Developer Survey and the GitHub State of the Octoverse Report.
- Investigate industry adoption. Which prominent companies and startups are using the tech stack?
- See search engine trends. Use tools like Google Trends to see how often specific technologies or programming languages are being searched for on the internet.
- Review historical data to see if the tech stack has grown or declined in popularity. Trends can reveal long-term popularity.
- Research job market demand. The more job opportunities for a particular tech stack there are, the more likely it is in need.
- Examine GitHub repositories related to the tech stack you’re interested in. Look at the number of stars, forks, and contributors. Active and well-maintained repositories are indicators of popularity.
Step 5. Create a prototype to test the tech stack
To ensure the chosen tech stack is the right fit, build a minimum viable product (MVP) or a prototype to test its capabilities. Here’s a basic framework to help you efficiently evaluate the suitability of the new tech stack without dedicating too much time and resources:
- Define the objectives of building a prototype. What aspects of the tech stack do you want to test?
- Limit the prototype to the most critical aspects of your project’s requirements;
- Select a simple use case or a representative feature from your project that highlights the capabilities of the new tech stack;
- Identify the resources you need, including developers, data, and tools;
- Create a Minimalistic User Interface (UI) that allows you to interact with the selected use case. This can be a simplified web page or application screen;
- Implement core functionality related to the chosen use case;
- Simulate real-world scenarios using sample or mock data. Avoid complex data generation processes; focus on the essentials;
- Test the prototype to ensure that the core functionality works as expected and see how it handles a basic workload. Identify and address any issues or bugs;
- Document your experience during the prototyping process, including challenges faced and solutions found. This documentation can be valuable for future reference.
- Gather feedback from your development team and stakeholders. Ask for their opinions on the ease of development and the feasibility of the tech stack;
- Evaluate the prototype against your objectives. Does the new tech stack meet your project’s needs? Assess whether the benefits outweigh the challenges and learning curve.
Need help in selecting the best tech stack?
Describe your project and business goals, and we will return to you with optimal options.
Write usTypes of tech stacks
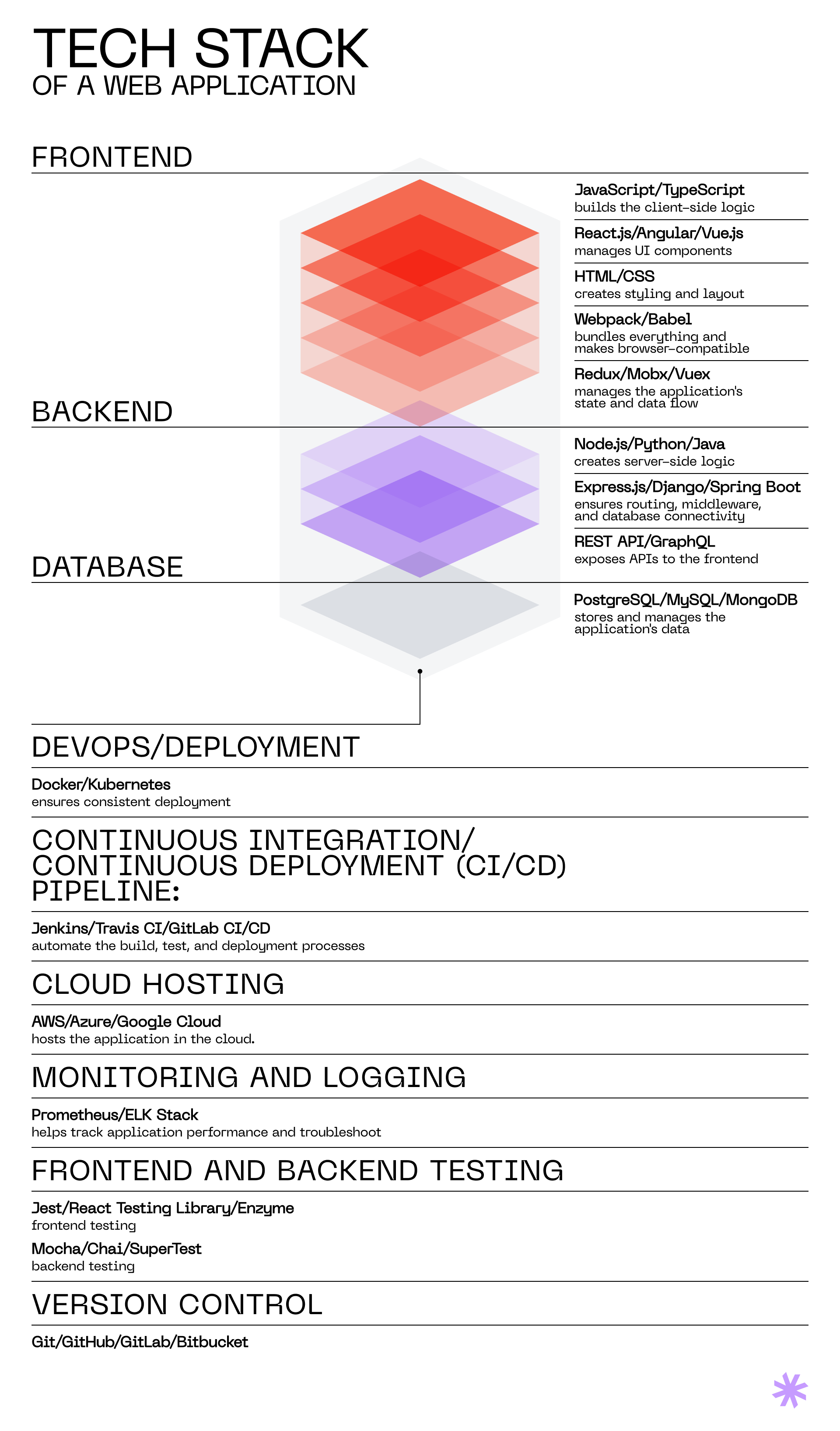
Most software applications follow a client-server model. In this setup, user devices connect to central servers over a network to communicate rather than talk directly to each other. These applications typically consist of two parts: the client-side (or front-end) and the server-side (or back-end), with different technology stacks involved in their development.
These tech stacks can be divided into three main categories:
- Front-end technology stack, also called client-side tech stack, refers to the set of technologies and tools used to build and run the user interface (UI) of an application. This is the layer that enables users to interact with an application. Developers use different web app tech stacks for client-side development, depending on whether it’s for the web or mobile.
- Mobile development tech stack is technically a component of frontend development. But because it requires a distinct set of technologies, we’ll discuss it separately in this article.
- Server-side tech stack, also known as the back-end tech stack, combines technologies and tools used to handle tasks like processing requests from clients (front-end), interacting with databases, implementing business logic, and managing server infrastructure. There isn’t much difference between the technologies used for web and mobile server-side development.
There is also a middleware layer. This is software that connects the back-end and front-end of an application. It facilitates data parsing, communication, and management between the application and the server or database.
Middleware includes things like application servers, web servers, content management systems, and other tools that support application development. Since this layer isn’t directly involved with building the application business logic, we won’t delve into it in this blog post.
Separately should be said about full-stack tech stacks, such as MEAN, MERN, and LAMP. These are collections of languages, frameworks, and tools that cover all layers of application development. For instance, the MEAN stack comprises MongoDB (a database), Express.js (a framework for Node.js on the back-end), Angular (a front-end framework), and Node.js (a back-end language). These technologies are bundled together because they are all based on JavaScript and offer flexibility and lightweight solutions.
However, while MEAN, MERN, and LAMP are established tech stacks, they might not be the ideal choice for every project. Your development team may need to create a unique tech stack tailored to the specific requirements of your software solution.
Now, let’s see how to choose a tech stack for each application layer.
Front-end tech stacks
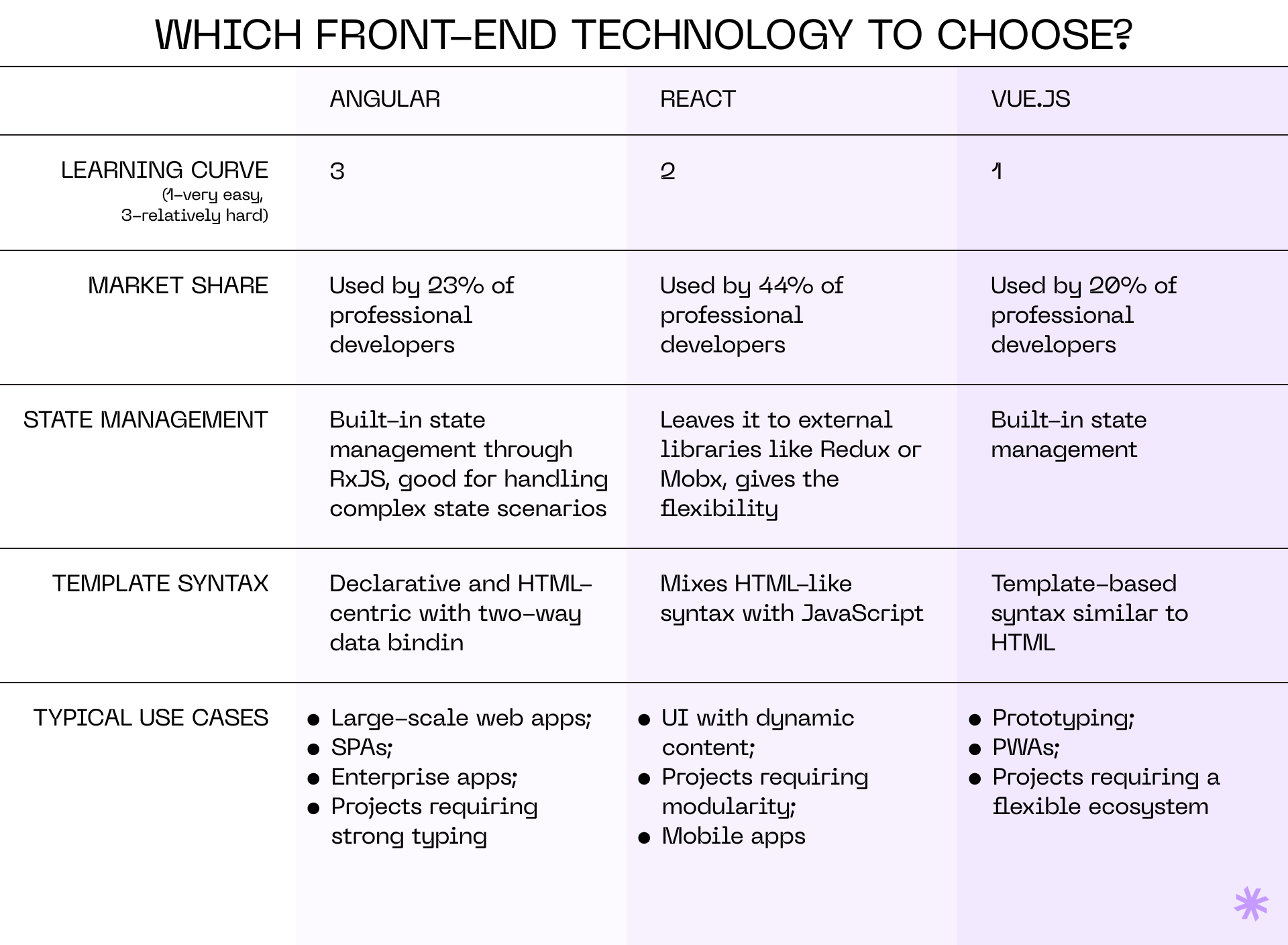
Angular, React, and Vue.js are the top popular technologies for building interactive web pages. They all have vibrant ecosystems with active communities, extensive documentation, and various third-party libraries and tools. Their component-based structure promotes code reusability, maintainability, and a structured way of building user interfaces, making them the best tech stack candidates for web apps.
Here’s a closer look at what makes each technology stand out:
- Angular is a mature and well-established framework maintained by Google. As part of a web app tech stack, it provides solutions for various aspects of application development, including routing, forms, and state management. The framework offers a built-in dependency injection system, simplifying component management and their dependencies. One of its drawbacks, though, is a steep learning curve, which might limit the number of developers proficient in this technology. It also tends to be verbose, potentially leading to larger codebases.
- React is a framework developed and maintained by Meta (formerly Facebook). It promotes a unidirectional data flow (one-way data binding), making it easier to understand and debug the application state. The framework can be used to build mobile apps with React Native, allowing code sharing between web and mobile applications. On the con side, React primarily focuses on the view layer, which can lead to a need for third-party libraries or custom routing and state management solutions. Furthermore, developers must use JSX (JavaScript XML) in React, which requires getting used to.
- Vue.js is known for its simplicity and ease of learning. It’s very flexible and can be used for various projects, from simple widgets to full-blown single-page applications (SPAs). At the same time, it is a newer framework compared to Angular and React, so it may offer fewer third-party libraries and plugins for specific purposes. Moreover, Vue.js lacks corporate backing, which may raise concerns about long-term stability.
Mobile development tech stacks
As we said earlier, tech stacks for mobile development are technically front-end since there isn’t much difference between tools used to create the backend layer for web and mobile software.
Yet, front-end development for mobile is additionally categorized into native, hybrid, and cross-platform development. The tech stacks for each of these categories vary in objectives, features, required resources, and budgets. Let’s take a closer look at them:
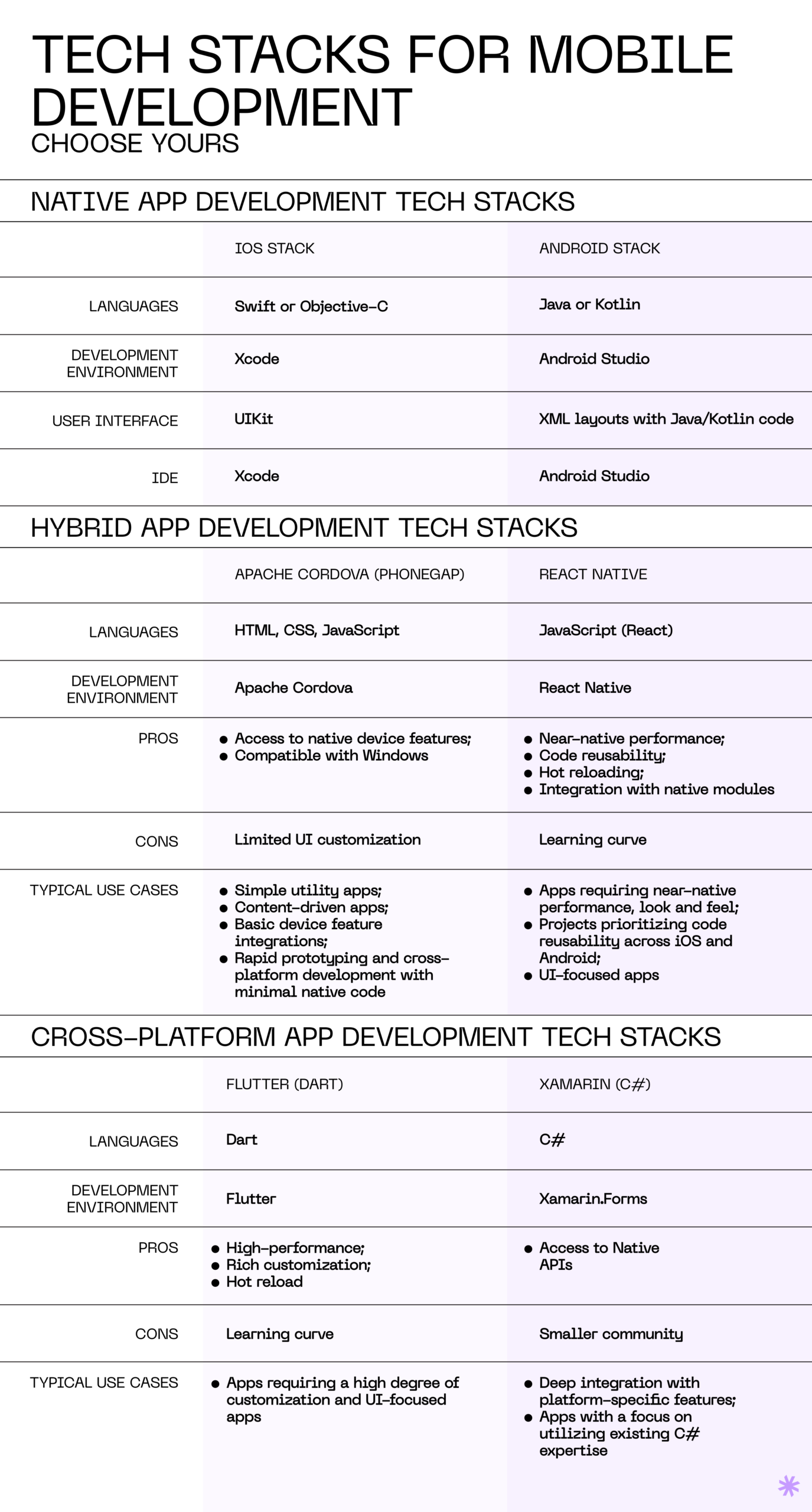
Native app development tech stacks
Native app development involves creating apps for a specific platform, such as iOS or Android, using the official software kits (SDKs).
- iOS native stack consists of Swift or Objective-C programming languages, an X-code development environment, and UIKit for the user interface building.
- Android native stack includes Java or Kotlin languages, Android Studio, and XML layouts with Java/Kotlin code for the user interface.
Hybrid app development tech stacks
Hybrid apps are built using web technologies wrapped within a native container. Two popular tech stacks for hybrid development are:
- Apache Cordova (PhoneGap) employs HTML, CSS, and JavaScript languages with frameworks like Cordova, PhoneGap, or Ionic. This stack offers pre-built plugins for various device features and functionalities, speeding up development. However, achieving a truly native look and feel can be challenging.
- React Native stack works with React or JavaScript language, coupled with the React Native framework. React Native apps are compiled into native code, delivering near-native performance and responsiveness. The hot-reloading feature permits real-time viewing of code changes in the app, enhancing development and debugging. However, developers new to React may face a learning curve when getting started.
Cross-platform development tech stacks
Cross-platform development tools enable developers to write code once and deploy it across multiple platforms. The top popular tech stacks in this category are:
- Flutter (Dart) stack uses Dart programming language and the Flutter framework. It provides high-performance, natively compiled code and an extensive widget library for building custom UIs. Nevertheless, it may have limited access to some platform-specific features due to its relatively small developer community.
Xamarin (C#) relies on the C# language and the Xamarin.Forms framework. It offers robust integration with Visual Studio and provides access to native APIs and device features. However, developers may need to write platform-specific code for some features.
Back-end tech stacks
When building the data access layer of software, most developers opt for Ruby on Rails, Express.js, and Django. These three technologies have gained popularity because they enable adherence to the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern, which makes development more straightforward. They are also open-source and compatible with various operating systems. Additionally, each of them boasts a thriving community.
Let’s delve into the distinct advantages and drawbacks of each technology:
- Ruby on Rails (RoR) emphasizes Convention over Configuration (CoC) and the Don’t Repeat Yourself (DRY) principles, enabling developers to build applications quickly with less boilerplate code. It offers many built-in tools and libraries for everyday tasks, boosting developer efficiency. RoR also includes built-in security features, guarding against SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. On the other hand, RoR may not be the best choice for CPU-intensive applications and can be resource-intensive.
- Express.js is a minimal and flexible web application framework for Node.js, a runtime environment widely used for developing server-side apps in JavaScript. Express.js simplifies the development process by providing a robust set of features for handling HTTP requests, routing, middleware integration, and more. Yet, its lack of strict structure and conventions can lead to inconsistencies and maintainability challenges in larger projects, especially when multiple developers are involved.
- Django follows the “batteries included” philosophy, providing many built-in features and libraries for common needs, including security measures. The framework’s high-level abstractions simplify complex and repetitive tasks, streamlining development and improving code quality. Its Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) makes database interactions easier by allowing developers to work with Python objects instead of raw SQL. However, Django may introduce unnecessary complexity in elementary projects and incur performance overhead due to its high-level abstractions.
| Ruby on Rails | Express.js | Django | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Rapid development High productivity Scalability Good documentation Security | Lightweight and unopinionated Flexible middleware system High performance Extensive ecosystem | High-level abstractions Rapid development Security ORM |
| Weaknesses | Learning curve Poor performance for CPU-intensive tasks Opinionated Resource-intensive | Limited built-in features Requires manual setup Potential for inconsistent code quality | Learning curve Complexity Opinionated Performance overhead |
| Typical use cases | Prototypes and MVPs CMS and content-driven websites E-commerce platforms API development | API development SPAs Real-time applications Microservices | Data-intensive apps CMS and content-driven websites E-commerce platforms |
Benefits of having the right tech stack
- Effective team communication
When a team uses a standardized tech stack with the same programming languages, frameworks, and tools, it fosters collaboration, knowledge sharing, and mutual support among team members. This, in turn, improves teamwork as developers can understand and contribute to each other’s code more effectively.
Additionally, a consistent tech stack often results in well-documented best practices and coding guidelines. These documents serve as references, helping the team stick to coding conventions and make informed decisions.
- Improved product performance
A well-chosen tech stack includes technologies that boost your application’s efficiency and speed. It can efficiently handle a growing user base and increasing data loads. Moreover, a good technology stack comprises tools and technologies that receive regular updates, further enhancing your product’s performance.
- Cost optimisation
A uniform tech stack that your development team is familiar with ensures efficient work and faster code development than learning new technologies. This reduces labor costs related to development.
Furthermore, the relevant tech stack often includes technologies with active developer communities and robust support. It means developers can easily find solutions when issues arise, lowering troubleshooting and maintenance costs.
Lastly, modern tech stacks often come with automation tools for deployment, testing, and monitoring, leading to more time and cost savings.
Examples of successful tech stack choices
Deciding how to choose the appropriate tech stack is crucial to creating a sustainable and prosperous product that can adapt and expand in sync with its users. Many of today’s technology giants attribute a significant portion of their achievements to making the right tech stack choices.
To illustrate this, let’s examine the cases of Netflix and Airbnb as well as one of Syndicode’s clients:
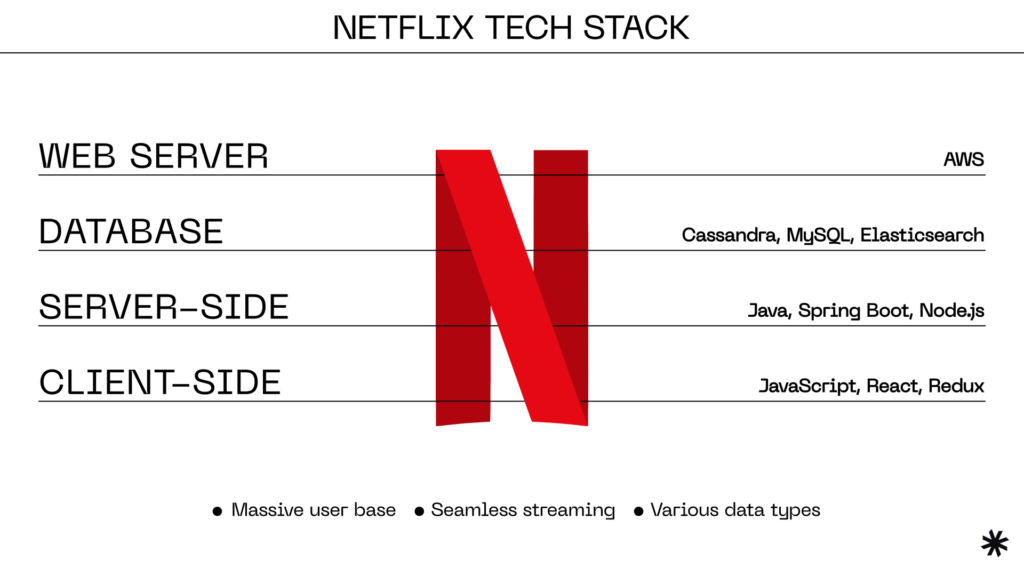
Netflix
- Frontend: Netflix uses JavaScript for its web development tech stack, combining React for user interfaces and Redux for state management.
- Backend: On the backend, Netflix relies on various technologies, including Java, Spring Boot, and Node.js. They also use a microservices architecture to break their applications into smaller, manageable components.
- Databases: Netflix utilizes various databases, including Cassandra, MySQL, and Elasticsearch, depending on the specific data storage needs of each service.
This tech stack offers Netflix several benefits that would be more challenging to achieve with other technologies, considering the company’s needs and resources.
Thus, the modular architecture simplified large user base maintenance and scaling. A combination of Java, Spring Boot, and Node.js for web application development enables seamless streaming on a global scale. React and Redux on the front end create a rich and interactive user experience vital for engaging users.
Finally, diverse databases efficiently handle various data types, from user profiles to content recommendations.
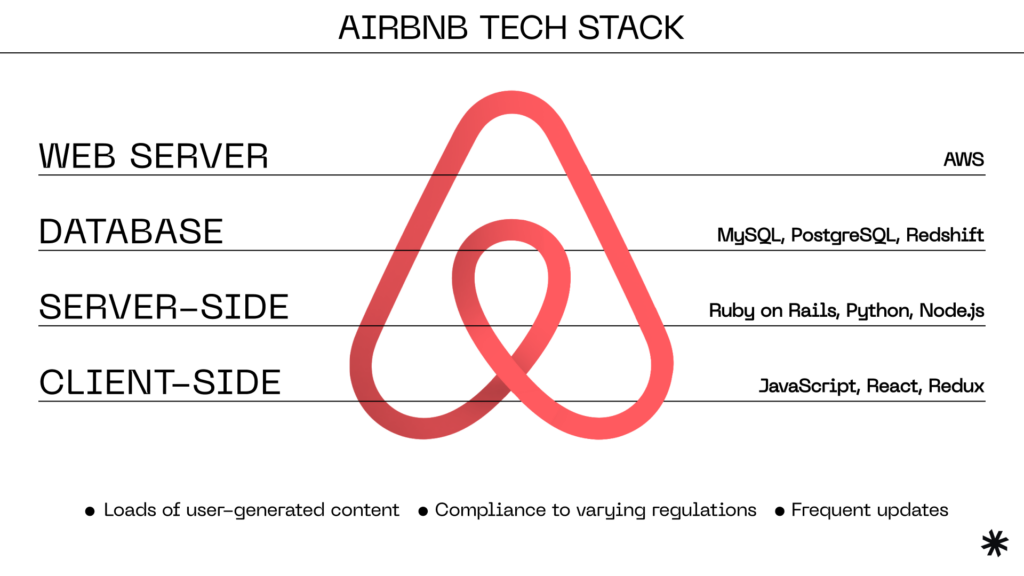
Airbnb
- Frontend: Airbnb’s frontend is primarily built using JavaScript, React, and Redux, ensuring a dynamic and responsive user interface.
- Backend: On the backend, Airbnb uses a mix of web technology stacks, including Ruby on Rails for the main website and services, Python for machine learning, and Node.js for some microservices.
- Databases: Airbnb relies on various databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Redshift, depending on the specific data storage and analysis requirements.
This unique combination of technologies offers the company a dynamic and interactive UI critical for user-friendliness. The company is also known for its frequent feature updates, made possible thanks to developer-friendly Ruby on Rails and Node.js environments.
The chosen databases, in turn, allow Airbnb to collect, analyze, and gain insights from large volumes of data, helping make data-driven decisions.
Harvest Inn
Harvest Inn is an Australian travel planning platform that serves as a hub for campervan stay options. It makes it easier for users to plan their journeys comfortably while ensuring compliance with local laws.
Syndicode developed the platform from scratch, with our team assisting the client in choosing the right tech stack. As a result, the platform was built using the following technologies:
- Frontend: Harvest Inn uses React with the Next JS framework, providing a strong foundation for the platform’s future growth.
- Backend: We chose Ruby on Rails for the platform’s backend. This framework allowed us to swiftly deliver the core functionality, ensuring easy maintenance and management. It also provides a stable base for future enhancements as the platform expands.
- Databases: PostgreSQL was an ideal choice for the platform as its powerful data-processing capabilities and intricate relationship structures perfectly matched the project’s requirements. Using this database ensured the smooth handling of any volume of transactions.
The resulting product was launched within a short timeframe, meeting the client’s requirements. It is secure, easy to maintain, and scalable.
Thanks to the use of mature technologies, the client has flexibility in choosing a development partner, whether they opt to continue working with Syndicode or explore other options.

Building a unique software product from scratch?
Leverage end-to-end software development services from a reliable and knowledgeable team.
See servicesHow much does a tech stack cost?
The cost of a tech stack can vary significantly based on multiple components. Here are some of the factors that contribute to the overall cost of a basic web application:
| Factor | Sample provider | Expense per factor |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | ||
| Hosting | AWS EC2 instances (2 m5.xlarge instances) | $151.84–350.40/month |
| Data storage | Amazon S3 and RDS | $300–919.04/month |
| Content Delivery Network | Amazon CloudFront | Starting at $0.11 per GB |
| Software licensing | ||
| Operating Systems | Included in AWS costs | |
| Database Software (RDS) | Included in AWS costs | |
| Development tools | JetBrains | $39.08–77.90/month |
| Development costs | ||
| Development team | Starting at $2,000/developer/month | |
| Third-party libraries and tools | Starting at $0.0/month | |
| Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) costs | ||
| Subscription services | Slack, Trello, etc. | Starting at $0.0/month |
| Security costs | ||
| Security tools | Starting at $30/month | |
| Penetration testing | Starting at $500 per scan | |
| Maintenance and support | ||
| Upgrades and patches | Varies based on the frequency of updates and complexity | |
| Technical support | Starting at $30/hour | |
| Data costs | ||
| Data storage | AWS S3 | $0.023/GB |
| Data transfer | AWS S3 | Starting at $0.0 |
| Licensing and compliance | ||
| Intellectual property licensing | Starting at a 5% royalty rate | |
| Compliance costs | Varies based on industry regulations and data protection requirements | |
| Training and certification | Varies based on business needs and the number of team members | |
| Monitoring and analytics | Amazon CloudWatch | Starting at $0.65/GB |
| Scaling and redundancy | Varies based on configuration | |
| Additional costs | ||
| Domain Registration | Starting at $5/year | |
| SSL Certificates | Starting at $8/year | |
| Consulting services | Starting at $30/hour |
Summary: how to choose a tech stack
To choose a suitable technology stack for web development, it’s essential to consider several factors:
- Project requirements: start by understanding your project’s specific needs and goals. Different projects may require different technologies to meet their objectives.
- Team expertise: assess your development team’s skills and expertise. Choosing technologies your team is familiar with can lead to more efficient development.
- Tech stack scalability: think about the scalability requirements of your project. Will the chosen tech stack support your project’s growth and future needs?
- Community support: check the level of community support for the technologies you’re considering. A strong community can provide valuable resources and assistance.
Evaluate factors like compatible programming languages, frameworks, and database options when deciding.
If you require guidance from an independent software development company, Syndicode can provide a tech stack assessment tailored to your project’s unique requirements and your team’s expertise. Our specialists excel in various technologies and have a proven track record of creating customized software solutions that align with our client’s business objectives.
Feel free to reach out to us through the contact form to describe your needs, and we will respond with suitable options in less than 24 hours.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Which tech stack is the best?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of which combination of languages and frameworks forming a stack is the best because the choice of a web development tech stack depends on many factors. When deciding how to select a technology stack, you should consider your project requirements, team expertise, budget, industry, and trends. Moreover, it’s worth comparing different tech stacks, assessing their scalability and community, and consulting with experts or experienced software developers.
-
What are the components of a tech stack?
A typical technology stack consists of two main components: the client-side (front-end) and the server-side (back-end). The front end includes a programming language and a development framework. The back-end additionally encompasses databases and supplementary technologies, such as libraries, containerization tools, and hosting platforms. In addition, a software development project’s tech stack may include testing frameworks, DevOps and CI/CD tools, and analytics. It’s important to pick the right components that best suit your project’s needs and align with your team’s skills.
-
Which language is best for web development?
There isn’t a single “best” language or tech stack for web development because the choice of language depends on various factors, including the project’s requirements, your team’s expertise, and your development goals. For example, web development technologies for a single-page application may include JavaScript and its frameworks. If you need a content management system, PHP or Python with a CMS framework might be more suitable. Consider factors such as your project scalability requirements and available resources when making your choice.
-
Is it possible to migrate to a new tech stack?
Yes, it is possible to migrate to a new tech stack, but it can be resource-intensive, time-consuming, and may come with associated risks. It’s essential to have a well-defined plan, engage experienced developers, and thoroughly test the application at each migration stage to minimize disruptions. Additionally, consider creating backups and rollback plans in case unexpected issues arise during migration. Basically, migrating to a different technology stack means redeveloping an application using other technologies.
-
What are the risks of choosing the wrong tech stack?
Choosing the wrong tech stack for a software project can lead to development delays, higher costs, poor software performance, limited scalability, security vulnerabilities, vendor lock-in, and maintenance challenges. To mitigate these risks, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research, assess project requirements, and carefully consider the pros and cons of different tech stack options before making a decision. Additionally, involving experienced developers and conducting pilot projects or prototypes can help validate the suitability of the chosen tech stack for your project.
-
How can I future-proof my tech stack?
To keep your software adaptable, scalable, and up-to-date in the ever-changing technology and business needs, opt for a tech stack that can easily adjust and grow as your requirements change. Look into open-source options and cross-platform frameworks. This will help you avoid getting stuck with one specific vendor and allow your software to handle more users and data when needed. Consider adopting an API-first approach to simplify connecting your software with external services and technologies as required. Keep up with industry trends and emerging solutions. You can follow relevant news sources and participate in developer communities. Regularly update your project’s technology stack with the latest releases, security fixes, and bug patches. If it’s time to move to a new stack, create a detailed plan for the migration. Before making major changes, consider running pilot projects or prototypes to confirm your chosen technology or approach.
